Acronym: EURL-PH-DIPE
Title: European reference laboratory network for EURL for public health in the field of Diphtheria and Pertussis
| Call | EU4H-2023-DGA-MS4-IBA |
| EU nr | 101194675 |
| Period | 84 months - 01.01.2025 to 31.12.2031 |
| Project budget | € 2,624,582.4 |
| VUB budget | € 389,888.99 |
| Contact | Dr. Eveline Van Honacker |
What is the EURL-PH-DIPE project about and what are the main goals?
This project is about two vaccine-preventable diseases that still circulate in EU-countries, pertussis and diphtheria. The European Center for disease Control (ECDC) launched a call for the establishment of a network of National Reference Laboratories (NRL) to meet a need for harmonization of methods, capacity building and professional exchanges of expertise and materials at the European level.
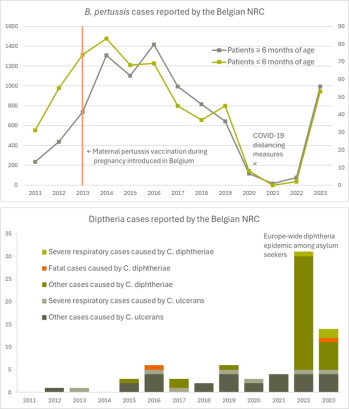
Pertussis (whooping cough) is a highly contagious respiratory disease mainly caused by Bordetella pertussis. In infants too young to be vaccinated, the disease is especially serious and still sometimes deadly. Despite extensive vaccination, pertussis remains endemic and epidemic worldwide, peaking every three to five years. After a very low prevalence due to social containment measures for Covid-19, an extensive epidemic is occurring in Europe since 2022.
Diphtheria presents mainly as a severe respiratory disease with systemic complications) e.g. cardiac and neurological symptoms), or a cutaneous infection. It is caused by toxigenic corynebacteria; Corynebacterium diphtheriae, highly contagious among humans, and the zoonotic C. ulcerans, only exceptionally transmitted between humans but occasionally acquired after contact with domestic animals (mainly cats and dogs), cattle, or sometimes wild animals. This disease became very rare in Europe, but in 2022 and 2023, an increase of cases was observed, of which the majority were diagnosed in migrant-related facilities.
How does an ideal vaccination program look like?
Both diseases are included in the basis childhood vaccination schemes in all European countries, followed by life-long boosters. However, both present shortcomings.
Pertussis immunization, both after vaccination or natural disease, is waning after a few years and mild, often unrecognized, pertussis episodes manifesting as cough, occur at any age, resulting in a reservoir of contamination for children too young to be vaccinated. In children less than one year old, pertussis has an atypical course, with few coughs but episodes of potentially fatal breathing pauses (apnea). Since 2013, the Superior Health Council advises a booster vaccination in pregnant women, to transfer immunity through the placenta and provide passive protection until infant vaccination can be provided. Unfortunately, maternal vaccine coverage is still too low, due to vaccine hesitancy.
Diphtheria immunization is very complete in Europe, but migrants from countries where vaccination programs were disrupted by war and other societal problems often did not receive childhood vaccinees and can be a source of infection for insufficiently immunized adults. Indeed, a recent serological survey demonstrated that up to 82% of adults aged 40 to 59 years lack the protective level of diphtheria antibodies in many European countries.
What will be the broader societal impact of EURL-PH-DIPE?
This EURL project will enhance protection and preparedness against pertussis and diphtheria in Europe, through different tasks aiming to improve functions of each NRL, and by providing guidance and help to both ECDC and NRLs.
What is VUB’s role in the EURL-PH-DIPE consortium?
The Belgian National Reference Centers (NRC) for pertussis and diphtheria are both coordinated by the laboratory of microbiology of the Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussels (UZB). They combine our expertise on the detection and characterization of B. pertussis, the agent of pertussis (whooping cough) and C. diphtheriae and C. ulcerans, the agents of diphtheria, with the expertise of the laboratory of immunology of Sciensano on the immunological response to these pathogens.
In the frame of this European Reference Laboratory led by Finland and in collaboration with France and Germany, UZB will organise two rounds of External Quality Assessments for B. pertussis detection, give scientific advice and technical support and organize training activities to other NRCs and ECDC, and organize scientific meetings.